Fiber Optic cable — Channel Capacity:
Frequency = Speed of Light (m/s) / Wavelength (nm)
C-Band(Conventional Band): 1530 nm to 1565 nm
Spectrum is Available in C Band:
$$
(\frac{299792458}{1530} - \frac{299792458}{1565}) \times 10^9 = 4.4 THz
$$
Flex-grid
Flex-gridremoves the fixed cubbyhole walls and lets the service provider define the spectral width of each wavelength independently.The optical spectrum is no longer pre-partitioned into
96 fixed slots of 50 GHzbut rathera continuous 4,800 GHz wide block of spectrum.the emergence of
Flex-gridallows the service provider tocarve the optical spectrum of their fibertotransport wavelengths of various spectral widths.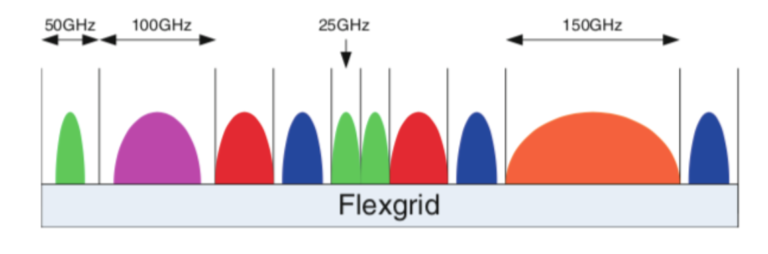
Spectrum planning with Flex-grid
The flexibility of Flex-grid offers a great benefit but it can also be a bit of a double edge sword. If channel assignment is not properly planned, it can lead to
stranded spectrumwithin the optical band.Wavelengths typically require at least a 50 GHz spectral width in order to provide a minimum of 100 Gb/s capacity over a typical metro DWDM network. An operator should be careful in ensuring that they are not leaving unassigned spectrum components between wavelengths that are not at least 50 GHz. The presence of small slices of unusable spectrum is commonly referred to as
spectrum fragmentation.The emergence of unusable stranded spectrum can actually occur over time. Optical circuits are dynamically created and deleted and this dynamic nature can unintentionally create spectrum fragmentation.